business model innovation
Business model innovation increases an organization's success with existing products and technologies.
Crafting a compelling value proposition can propel a new business model to scale up customers and create a lasting competitive advantage.
It all starts with mastering the key customers.
Before I dive into it, below is a visual representation of what I’ll cover in this issue!
Today’s Issue is Made Free to You by Koop
Slash SOC 2 & Insurance Costs by 50% with Koop
Koop helps businesses like yours save up to 50% on SOC 2 automation and business insurance.
Koop not only simplifies achieving compliance like SOC 2 but also ensures you have optimal coverage, allowing you to focus on what truly matters—growing your business.
The importance of business model innovation
In the last years, I've been dissecting business models of any type, and companies of any size. At the same time, I've been talking, interviewing, and discussing business models and business model innovation with dozens of entrepreneurs and practitioners.
I've been doing that for several reasons:
To gain a better understanding of businesses around me. As I had the option to gain a Ph.D. on the topic or to create my Ph.D. I went for the latter, and in the process, I thought to document it all on FourWeekMBA. Over time I wanted to create the business school I always dreamed of.
Business models enabled me to gain insights into how companies work holistically so that I could become a better digital entrepreneur.
Business modeling also helped me test the assumptions around the business I was trying to build, thus reducing the time or potential financial resources spent on a project doomed to failure.
In short, I found myself using business modeling for several reasons, all of which I believe are legitimate.
At the same time, while researching the topic with the mindset of an entrepreneur but the depth of reach of a Ph.D., I noticed how business model and business model innovation had become widely adopted concepts.
They were also (and probably for that reason) widely misunderstood.
Business model innovation is about increasing an organization's success with existing products and technologies by creating a compelling value proposition that allows the organization to scale up customers with a better operating model.
At its core, business model innovation is a subtle change that, as it becomes hard to dissect from the outside world (in many cases, business model innovation is detected when an organization has achieved massive success), is also hard to copy.
Thus, in a world where technology has become, in part a commodity business model innovation can make a huge difference.
Before we move forward toward deciphering and dissecting business model innovation, let's bust three myths that exist in the entrepreneurship world, especially in the era of digital business models.
Business model innovation enables you to create competitive moats
As technology becomes over time a commodity, creating a lasting advantage requires business model understanding, experimentation, and execution.
That's because business model innovation shifted the focus from the competition, which is what, in the last decades, we've all been looking at with frameworks like Porter's Five Forces to customers.
Without going through all the reasons why that happened today, business model innovation has become more important than technical innovation.
Here's a quick caveat before we move on.
When I say that the focus has shifted to customers, it doesn't mean you don't need to understand your competition. It just means you must start with customers and their problems.
Only after that do you want to move to competition and what existing alternatives exist.
A multi-faceted concept
Although we like to give a single definition to each of the concepts we know, those concepts will adapt based on their context.
In short, it is fine to have multiple definitions of the concept based on each practitioner's objective.
Therefore, it's okay that a concept translated into several fields will have different meanings.
Thus, let's see some of those meanings.
Analysts use business models to produce financial analyses
Business modeling can be seen as dissecting any organization and business for analysts and people trying to understand those businesses better.
Business and financial analysts use business modeling to better understand tech companies and to provide investment recommendations, financial reviews, and advice.
Academics study business models for the sake of classifying things
For academics, a business model might be just a holistic way to describe a business. The purpose of an academic might seem more rigorous than an entrepreneur's.
The academic has to prove that a business has certain features that make it different from or similar to other businesses.
From those features, the academic will derive classifications that, as they become more and more complex, only live in theory land.
The research, therefore, doesn't necessarily have a practical purpose.
Instead, the goal is to uncover universal classification systems for things in the real world.
As such, they might lose a practical application.
Most people confuse business models for business plans
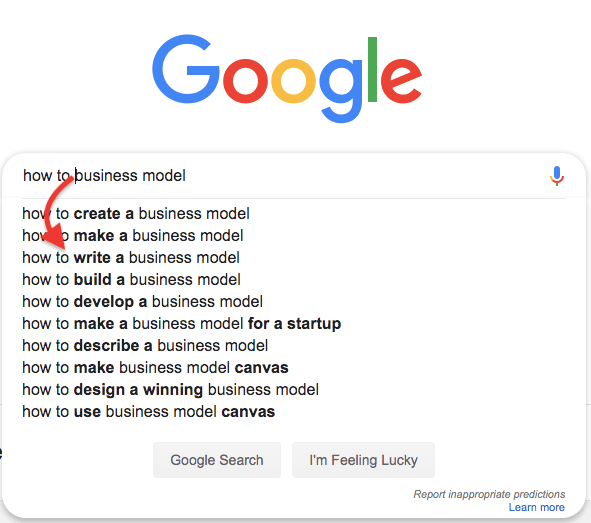
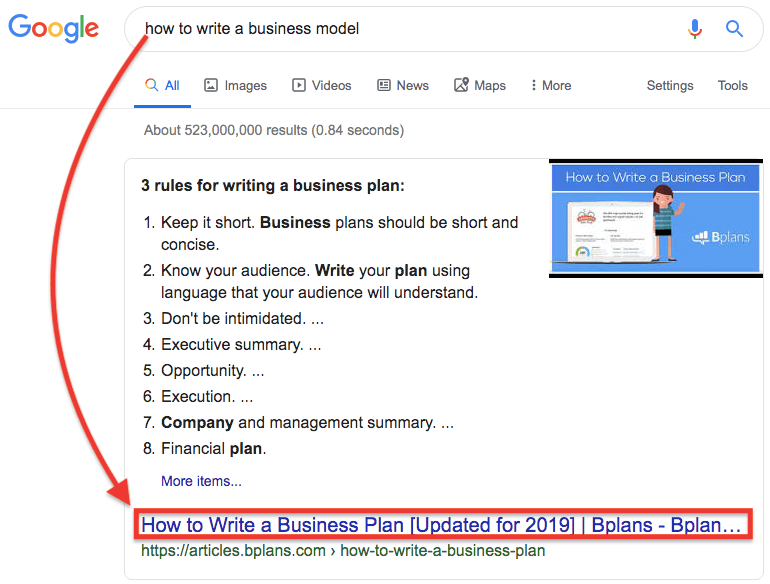
Among the top results, Google suggests "How to write a business model" when typing "how to ... business model. When you click on the result that Google suggested, see what happens.
When you click on the Google suggested result for "How to write a business model," you get "How to write a business plan."
For most people (those who didn't study the topic), business models often resonate with business plans. I noticed it when I started to research the topic.
As Google makes the search data and behaviors of billions of people accessible, it also adapts to those search behaviors.
To my surprise, in the past, I noticed how for the query "how to write a business model," Google served results around "how to write a business plan."
I've learned to appreciate those "mistakes" as Google is a commercial search engine.
And as such, it follows what most people search for.
If people collectively think a business model is a business plan, Google might make that true.
This means that if you are an entrepreneur searching for valuable resources, either you are lucky to find the resource you need, or you might end up writing a hundred-page business plan which won't help much with your business.
If at all, it will prevent you from starting it.
As you will start making things more complicated than they should be.
Startups confuse business models for monetization strategies
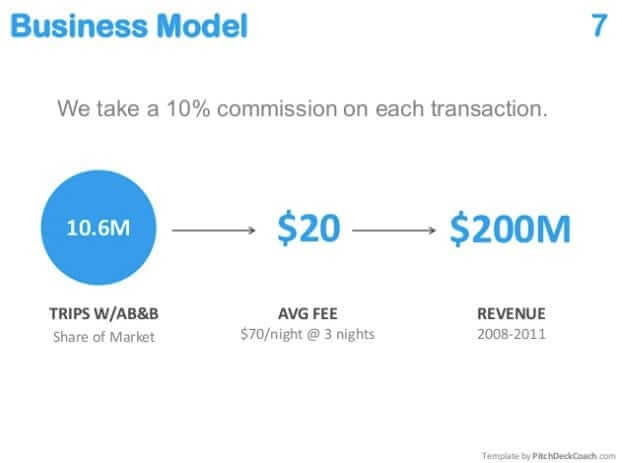
An example of how Airbnb "confused" its business model for its monetization strategy (Slideshare)
How WeWork described its business model in the report before the IPO. You might notice that they're talking about their revenue generation strategy. (WeWork Financials)
And for many startups, the business model resonates with monetization strategies. I'm not saying this is right or wrong; it's just what it is.
Overall, that is fine.
Startup pitches or financial forms are often also marketing tools meant to communicate and simplify a concept.
Thus, if most investors want to know about your business model but what they mean is how you make money, that is fine to simplify it.
However, as an entrepreneur, if you do believe that a business model is how you make money, that might limit your options, as all day long, you'll think about monetization strategies rather than having a more holistic and strategic approach.
Business model innovation is an experimentation mindset for entrepreneurs
Business model design is not about sketching a plan on a piece of paper but rather a mindset of experimentation.
In business modeling, you can manufacture experiments (business models and business model variations) that enable the entrepreneur to test the assumptions around the business quickly, cheaply, and with minimum effort.
It is important to start testing (as practitioners like Ash Maurya highlighted) from the riskiest assumptions.
Those assumptions are assumptions for which the business might not become sustainable over time.
Some of the riskiest assumptions, such as monetization strategy or key customer understanding, need to be tested quickly.
An entrepreneur is not a scientist
An entrepreneur has different goals than a scientist, where the scientist might try to uncover more universal truths.
The entrepreneur needs to experiment with the business model to test the assumptions, uncover market opportunities, reduce the time to market, and eventually build a valuable business.
In short, an entrepreneur is a market-driven animal, rather than starting from theories to find if that is true through experiments.
An entrepreneur starts with a problem and then returns to theory to understand the underlying assumptions preventing the business from succeeding.
Once those assumptions have been streamlined, they can be tested so that the entrepreneur can move on and make the product or service in target with the market.
Business model innovation is, at the same time, a mindset, a framework, and a set of tools for entrepreneurs
Business model innovation, therefore, can be seen as a mindset, framework, and a set of tools for entrepreneurs to build relevant businesses in today's marketplace.
Myth one: the best product wins
When you get online and want to look for something but are unsure what it is, chances are you'll land on a white page with a small search box on it. That is the Google search results page.
Why, in the first place, do you get there?
Well, you get there because Google is an incredible product. It can find anything on the web at a super-fast speed.
Yet, is Google the best product out there? And how do we define best?
Well, Google is a great search engine that can give you relevant results for any question, and it also benefits from network effects.
In short, one reason Google is good enough at intercepting search intents is that billions of people around the world use it each day.
At the same time, Google is a decent product for what it gives us back (and it is free), but it also has drawbacks.
For instance, in an experiment, an SEO expert tried to rank a Latin Language site (a language used by ancient Romans, no longer in use), and guess what? It did that successfully.
This is not to say that Google is not a good search engine.
Google is today the most widely used search engine on earth, and part of the reason is its distribution strategy.
Since its scale-up phase, Google aggressively acquired deals that made it the tech giant we know today.
However, only a few people realize it, and it is easy to think—especially in tech—that the best product wins.
A great product with a lack of distribution strategy won't go far.
Myth two: technology is what gives a competitive advantage
Peter Thiel, the former CEO of PayPal, has shifted an important business paradigm.
As the common business thinking goes, "Be the first, and you'll probably win over time."
This is called business jargon, first-mover advantage.
Peter Thiel, instead, pointed out a critical paradigm, especially in the tech industry, which is the last-mover advantage.
In other words, companies that come later, especially in the tech industry, can win over existing organizations, even when those were the first movers.
For instance, Google and Facebook were not the first to enter the search and social media space, but they dominated it.
What happened there? The answer is business model innovation!
Myth three: business model innovation is just about how you make money
It was a great search engine when Google came out of the Stanford dormitory where the two P.h.D. had invented it. Many argue it was 10x better than competitors.
Yet it wasn't financially successful until it managed to design an innovative business model via a couple of years of trial and error.
In short, Google introduced an auction system for advertising to remove the inefficiencies of how advertising had worked for decades.
That was not the primary innovation. Indeed, another search engine called Overture was already doing it successfully.
Therefore, Google innovated by introducing a few critical parameters that allowed advertisers to appear above Google text-based ad results.
In other words, it wasn't enough to be offering a higher bidding rate on a keyword.
Google crossed that with a few other parameters, which allowed it to show, on top of the ads space on Google results, those that were most relevant and had a higher click-through rate.
Even though it might sound trivial now, as the whole web, after Google has been built on the premise of click-through rate, it was not back then.
That business model innovation was critical to Google's economic hypergrowth, scale, and domination.
Business modeling isn't a simple concept, and in most people's minds, that is about how you make money. However, business modeling is way more than that.
It is how you make a great product or service so that your customers keep returning.
It is about how you make that product or service scalable. And how you keep making financial sense of your business over time.
But also the value proposition you can deliver to critical partners, which is crucial to your business success!
Thus, even though business model innovation can change how you charge your customers and make money, it can also involve other critical aspects of the business that will allow you to scale up.
There isn't a single path to business model innovation, but there are a few critical questions to ask.
What kind of questions do you need to ask with business model innovation?
To understand how to innovate a business model you might want to think along the lines of how to tweak and redesign your value chain, cost structure, key partners, and, in general, what can help you scale:
How can I design a better value chain?
Can I improve the existing cost structure?
What is the distribution channel that can accelerate growth?
Why is my company experiencing bottlenecks in certain areas?
Is the organizational structure helping the company to grow as it should?
Paths toward business model innovation
There isn't a single path toward business model innovation.
You can sometimes design a business model drawing from your previous experiences in that industry.
Other times, you'll have to figure it out along the way. Among the many paths to business model innovation, we'll see three paths that might be pretty interesting for your business.
Engineer an innovative business model from scratch
As Reid Hoffman points out in his book Blitzscaling Business Model, innovation is a crucial ingredient to success, especially in the digital space, where countless companies offer innovative tools and solutions on the market.
That's why, in some cases, business model innovation can be engineered before
This is what happened when I cofounded LinkedIn. The key business model innovations for LinkedIn, including the two-way nature of the relationships and filling professionals’ need for a business-oriented online identity, didn’t just happen organically.
As explained, Reid Hoffman used his understanding of the social networking world (he had founded a social network called SocialNet) to design an innovative business model for LinkedIn, which was acquired by Microsoft in 2016 for an astounding $26.2 billion.
In short, what gives a competitive advantage isn't any more technology alone but a combination of technology paired with an innovative business model.
Yet designing a business model isn't always possible beforehand.
Sometimes, you must experiment, reiterate, and find it.
Indeed, that is how you can engineer a business in most cases.
It's fascinating to read the history of successful businesses and think they were sketched on paper.
That only happens in hindsight.
In most cases, you figure it out along the way.
You know where you want to get, but how you will get there in the short term will depend highly on the context and landscape.
This is what the business engineer does.
With a long-term vision yet a short-term understanding of the landscape, the business engineer tries to build and scale businesses.
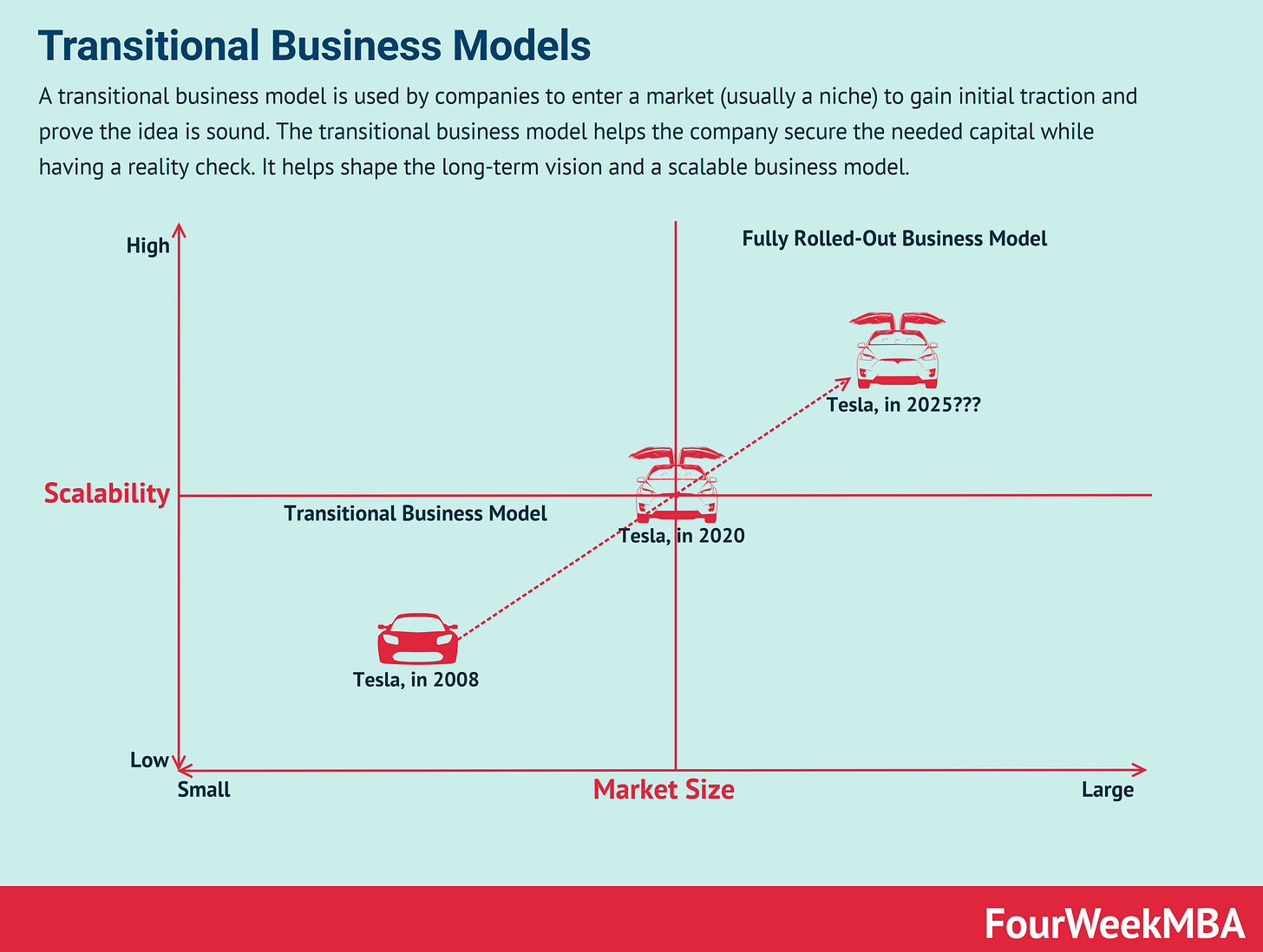
Thus, both use a transitional business model grounded in the current reality.
That enables a company to validate the market in the short term, put together a business model that works for the business's current scale, and create an option to scale.
Thus, the company has options to get larger and scale a business model to test to which extent it will work at the current scale and when new elements are needed to test it at wider scales.
In other words, business engineering requires a combination of understanding of product, distribution, and how this is integrated via technology at various scales!
Find an innovative business model along the way
When Google was scaling up, it didn't figure it all out right away.
Although the tech giant has incredible technology and products, it still lags behind in business model innovation.
When it finally figured it out, after a few trials and errors (Google was running out of investment money), it was a massive success.
When Google had to show its numbers when it got listed back in 2004, the company already made over three billion in revenues, a 155x growth in about four years!
In this scenario, you need to try and test many things before you can say that you have a business model that allows you to scale up sustainably and that makes sense financially.
In the end, if you find it, you've created a long-lasting competitive advantage!
Use business model innovation as a survival mechanism
Imagine if the next time you reserve an Uber ride, you'll see coming to a self-driven car.
Now, stop imagining. Indeed, Uber has been investing in self-driving cars since 2015.
Why would a company dominating an entire space make such a move?
Well, there are a couple of reasons. First, if self-driving cars become mass-adopted, Uber would be out of business.
This implies that Uber needs to be at the top of its game if It wants to thrive in the next era.
The second aspect is about business model innovation. Among its key partners, Uber has drivers across the world.
Yet those drivers also pose a significant threat to Uber's success.
Even though Uber might be pulling the plug or spinning off its self-driving cars business, this example shows how the company never stops experimenting with business model innovation.
Business units like Uber Eats, Express Pool, and Freight are all attempting to tweak an existing business model until it allows the company to become financially sustainable and at a massive scale.
Business Engineering as the Engine of Business Model Innovation
In the last decade, I've treated this blog as my real-live Ph.D. in business.
I believe that to drive value in the current business landscape quickly, you should combine a practical understanding of the real world, thourhg a lot of experimentation, and a set of heuristics to help you drive through the ambiguity of that world.
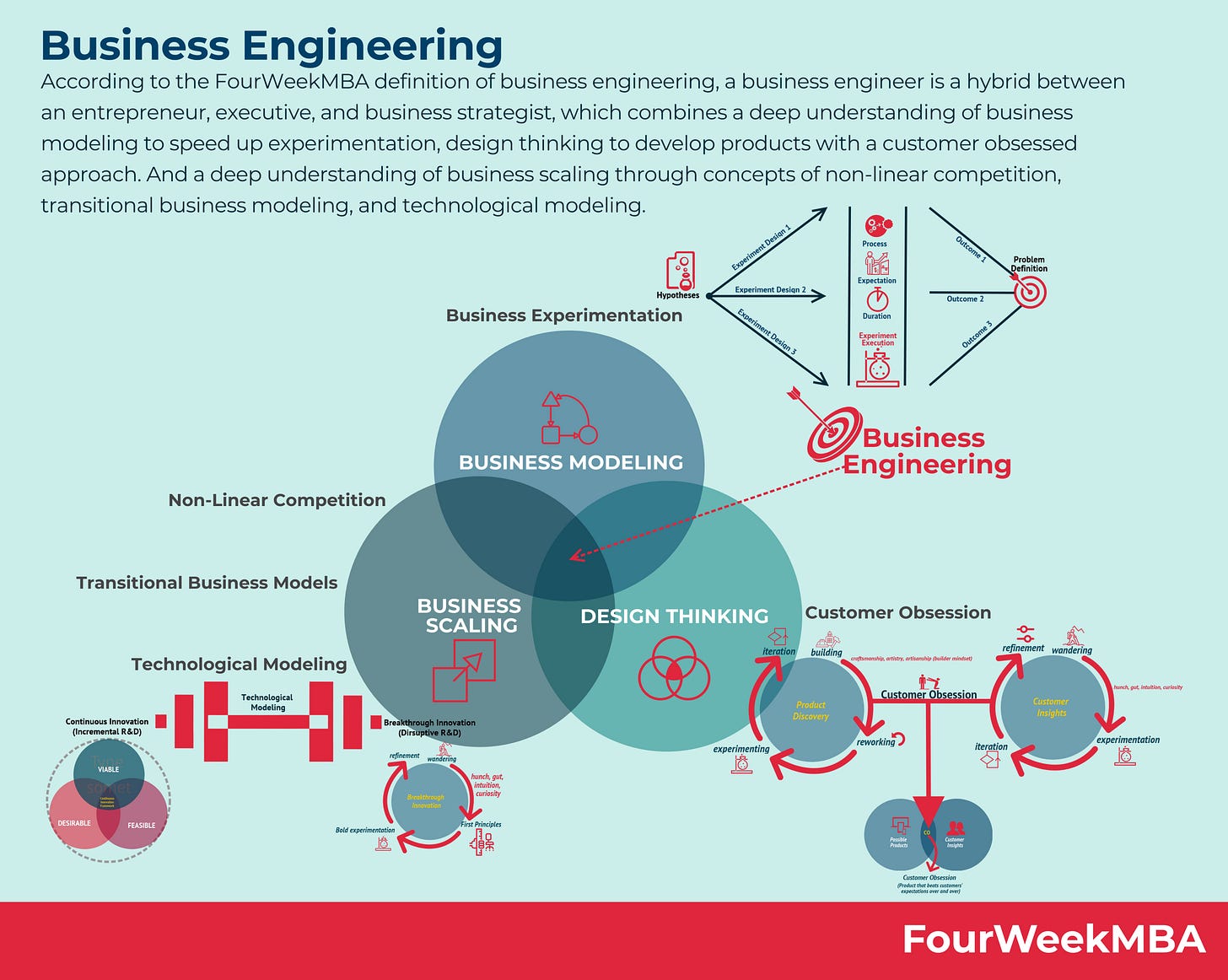
For that matter, I've built a discipline called business engineering.
Contrary to the traditional definition of business engineering (primarily about integrating technology in business processes).
Business engineering, as structured on FourWeekMBA, is a holistic discipline that aims to understand the changing business world by applying simple heuristics and an experimental framework.
To make sense of the real world in a way that enables you to build from scratch, grow, maintain, and innovate within startups and organizations.
Real World Case Studies
Netflix
Name of Business Model: Subscription Streaming Model
Key Elements: Monthly subscription, Original content production, Streaming on multiple devices
Outcome: Became a global leader in streaming entertainment, high subscriber growth
Tesla
Name of Business Model: Direct-to-Consumer Automotive Model
Key Elements: Online sales, Direct stores, Vertical integration
Outcome: Disrupted the automotive industry, significant market share in electric vehicles
Amazon
Name of Business Model: Marketplace Platform Model
Key Elements: Third-party sellers, Fulfillment by Amazon, Prime membership
Outcome: Became the largest e-commerce platform, high customer loyalty
Uber
Name of Business Model: Ride-Sharing Model
Key Elements: Mobile app for ride-hailing, Surge pricing, User and driver ratings
Outcome: Revolutionized urban transportation, global expansion into various services
Airbnb
Name of Business Model: Peer-to-Peer Lodging Model
Key Elements: Short-term home rentals, User reviews and ratings, Easy booking process
Outcome: Disrupted the traditional hotel industry, global presence and high user adoption
Facebook
Name of Business Model: Social Media Advertising Model
Key Elements: Free user access, Targeted advertising, Data-driven ad placement
Outcome: Became the largest social media platform, significant advertising revenue
Google
Name of Business Model: Ad-Supported Search Engine Model
Key Elements: Free search services, Pay-per-click advertising, AdSense network
Outcome: Dominated the search engine market, high ad revenue
Apple
Name of Business Model: Integrated Ecosystem Model
Key Elements: Hardware, software, and services integration, Strong brand loyalty, Premium pricing
Outcome: Revolutionized multiple industries, high profitability and market share
Microsoft
Name of Business Model: Subscription Software Model
Key Elements: Office 365 subscription, Cloud services, Regular updates
Outcome: Significant revenue growth, high customer retention
Spotify
Name of Business Model: Freemium Music Streaming Model
Key Elements: Free tier with ads, Premium subscription for ad-free experience, Personalized playlists
Outcome: Became a leading music streaming service, high conversion to premium subscribers
Slack
Name of Business Model: Freemium Team Collaboration Model
Key Elements: Free version to attract users, Premium features for enterprises, Integrations with other tools
Outcome: Became a dominant player in team collaboration, high enterprise adoption
Dropbox
Name of Business Model: Freemium Cloud Storage Model
Key Elements: Free storage with paid plans for additional features, Seamless file sharing
Outcome: Became a leading cloud storage service, high user adoption and retention
LinkedIn
Name of Business Model: Professional Networking Model
Key Elements: User profiles and connections, Job listings and premium features for job seekers and recruiters
Outcome: Became the leading professional networking platform, revolutionized job searching
YouTube
Name of Business Model: Ad-Supported Video Sharing Model
Key Elements: Free access to videos, Ad revenue sharing with creators, Content recommendation algorithms
Outcome: Became the largest video-sharing platform, significant ad revenue
Instagram
Name of Business Model: Visual Content Sharing Model
Key Elements: Photo and video sharing, User engagement through likes and comments, Influencer marketing
Outcome: Became a leading social media platform, high user engagement
Coursera
Name of Business Model: Online Education Platform Model
Key Elements: Partnerships with top universities, Free and paid courses, Specializations and degrees
Outcome: Expanded access to education globally, significant enrollment in courses and certifications
Canva
Name of Business Model: Freemium Design Tool Model
Key Elements: User-friendly graphic design tools, Free tier with premium features, Extensive template library
Outcome: Empowered non-designers to create professional-quality graphics, rapid user growth
Robinhood
Name of Business Model: Commission-Free Trading Model
Key Elements: No trading fees, User-friendly mobile app, Access to financial markets for average investors
Outcome: Disrupted the traditional brokerage industry, significant user growth and market impact
Patreon
Name of Business Model: Membership Platform Model
Key Elements: Creators set membership tiers, Recurring revenue for creators, Direct support from fans
Outcome: Empowered creators to monetize their content, significant growth in user base
Warby Parker
Name of Business Model: Direct-to-Consumer Eyewear Model
Key Elements: Online sales with home try-on, Designer eyewear at lower prices, Socially conscious business practices
Outcome: Disrupted the eyewear industry, high customer satisfaction and market share
Peloton
Name of Business Model: Subscription Fitness Model
Key Elements: Exercise equipment with subscription-based virtual classes, Engaging content, Community features
Outcome: Created a new market for at-home fitness, achieved significant growth and customer loyalty
Instacart
Name of Business Model: On-Demand Grocery Delivery Model
Key Elements: Partnership with local grocery stores, Personal shoppers, Delivery within hours
Outcome: Revolutionized grocery shopping, significant market share in the on-demand delivery space
Square
Name of Business Model: Payment Processing Model
Key Elements: Portable card readers, Simple fee structure, Easy setup for small businesses
Outcome: Enabled millions of small businesses to accept card payments, became a leading payment processor
TikTok
Name of Business Model: User-Generated Content Model
Key Elements: Short-form video content, Strong algorithm for content discovery, Viral challenges
Outcome: Became a global phenomenon with high engagement and rapid user growth
Pinterest
Name of Business Model: Visual Discovery and Bookmarking Model
Key Elements: Users discover and save creative ideas, Strong emphasis on visuals, Niche community
Outcome: Became a leading platform for visual discovery, high user engagement
Blue Apron
Name of Business Model: Meal Kit Delivery Model
Key Elements: Pre-portioned ingredients with recipes, Subscription service, Focus on quality and variety
Outcome: Popularized the meal kit industry, became a leading meal kit delivery service
WeWork
Name of Business Model: Co-Working Space Model
Key Elements: Shared workspaces, Community events, Flexible lease terms
Outcome: Became a global leader in co-working spaces, rapid expansion in major cities
Adobe
Name of Business Model: Subscription Software Model
Key Elements: Shift from perpetual licenses to subscription (Creative Cloud), Regular updates, Cloud-based tools
Outcome: Significant revenue growth, high customer retention and recurring revenue
Shopify
Name of Business Model: E-commerce Platform Model
Key Elements: Subscription-based SaaS platform, Extensive app ecosystem, Easy-to-use interface
Outcome: Enabled millions of small businesses to set up online stores, became a leading e-commerce platform
Duolingo
Name of Business Model: Freemium Education Model
Key Elements: Free access with optional paid features, Gamified learning, Wide range of languages
Outcome: Became the most popular language learning app, high user engagement and retention
OYO
Name of Business Model: Aggregator Model
Key Elements: Standardized budget accommodations, Strong branding, Technology-driven operations
Outcome: Became a leading budget hotel chain, rapid global expansion
Beyond Meat
Name of Business Model: Plant-Based Protein Model
Key Elements: Plant-based meat alternatives, Focus on taste and texture, Distribution through major retailers
Outcome: Pioneered the plant-based meat industry, significant market share and growth
Nespresso
Name of Business Model: Subscription Coffee Model
Key Elements: Single-serve coffee pods, Subscription service for regular deliveries, High-quality coffee
Outcome: Revolutionized the coffee industry, high customer loyalty and recurring revenue
Tinder
Name of Business Model: Freemium Dating App Model
Key Elements: Free access with in-app purchases, Swipe feature for matching, Subscription for premium features
Outcome: Became a leading dating app, high user engagement and revenue from in-app purchases
Glossier
Name of Business Model: Direct-to-Consumer Beauty Model
Key Elements: Online sales, Focus on community and customer feedback, Social media-driven marketing
Outcome: Disrupted the beauty industry, high customer loyalty and rapid growth
Lemonade
Name of Business Model: Digital Insurance Model
Key Elements: Online platform for insurance, AI-driven claims process, Monthly subscription
Outcome: Disrupted the insurance industry, high customer satisfaction and rapid growth
Etsy
Name of Business Model: Handmade Marketplace Model
Key Elements: Platform for handmade and vintage goods, Support for small businesses, Community-driven marketplace
Outcome: Became a leading marketplace for unique goods, high user engagement and sales
BuzzFeed
Name of Business Model: Digital Media Model
Key Elements: Free content supported by native advertising, Viral content creation, Data-driven editorial strategy
Outcome: Became a leading digital media company, high user engagement and advertising revenue
Stitch Fix
Name of Business Model: Personal Styling Service Model
Key Elements: Personalized clothing recommendations, Subscription box service, Data-driven styling
Outcome: Disrupted the fashion retail industry, high customer satisfaction and recurring revenue
Twilio
Name of Business Model: API-Driven Communication Model
Key Elements: Cloud-based communication APIs, Pay-as-you-go pricing, Integration with other platforms
Outcome: Enabled developers to build communication features easily, significant market share in cloud communications
Strava
Name of Business Model: Freemium Fitness Tracking Model
Key Elements: Free access with premium subscription for advanced features, Social network for athletes, Data-driven insights
Outcome: Became a leading fitness tracking app, high user engagement and premium subscriptions
Key Highlights
Understanding Businesses and Innovation: The author has been deeply involved in dissecting various business models and discussing business model innovation with entrepreneurs and practitioners. This has helped them gain insights into how businesses work and become a better digital entrepreneur.
Holistic Approach to Business: Business model innovation focuses on creating a compelling value proposition to scale up customer base and improve the operating model, rather than just focusing on technical innovation or competition.
Shifting Focus to Customers: Business model innovation shifts the focus from competition to customers. It involves understanding customer problems and needs before considering competition and alternatives.
Misconceptions and Myths: There are misconceptions and myths surrounding business models, including confusing them with business plans or monetization strategies.
Experimentation and Risky Assumptions: Business model innovation is an experimentation mindset that allows entrepreneurs to test the riskiest assumptions around their business quickly and efficiently.
Importance of Business Model Innovation: Business model innovation is crucial for success in the current landscape, where technology becomes commoditized, and it can provide a lasting competitive advantage.
Paths to Innovation: Business model innovation can be engineered from scratch, found along the way as a business grows, or used as a survival mechanism to adapt to changing market conditions.
Google's Example: Google's success wasn't solely due to technology; it innovated its business model by introducing an auction system for advertising, which significantly contributed to its growth.
Uber's Approach: Uber's pursuit of self-driving cars and experimentation with different business units like Uber Eats and Express Pool showcase a commitment to ongoing business model innovation.
Business Engineering: The author proposes a concept called "business engineering," which involves understanding the changing business landscape through heuristics and an experimental framework to build, grow, maintain, and innovate within startups and organizations.
Ciao!
With ♥️ Gennaro, FourWeekMBA