Google has been the first company to start the transition as an “AI-first” company, not in the 2020s, but already by 2017. Indeed, so much so that by 2018, the company had released Google Duplex.
Google was so far ahead, yet it got so far behind until, just a couple of weeks back, it finally started solidifying its strategy around three core pillars.
These pillars will work to transition Google into the current AI era in an excellent way. Yet, you might be surprised to figure out in this analysis that while search is Google's core business, it will also be the hardest to adjust to the current AI age!
While other verticals, both at an enterprise and consumer level, might propel Google in the coming phase!
Our NotebookLM AI hosts tackle the topic covered in what’s coming in Google’s AI Triad!
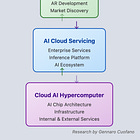
Google's Three Pillars of AI Leadership
Gennaro Cuofano identifies three core pillars driving Google's AI strategy:
Cloud AI Hypercomputer: An advanced infrastructure powered by Trillium TPUs, designed for large-scale AI training and inference.
AI Cloud Servicing: Enterprise-focused AI services enabling businesses to build, train, and deploy AI applications.
Consumer Integration: Embedding AI across Google's products, from Search to AR, fostering adoption and uncovering new opportunities.
Trillium TPU: The Engine of Google's AI Ecosystem
The Trillium TPU is a cornerstone of Google's AI strategy, with transformative capabilities:
Performance: Provides 4.7x higher compute performance and 3x inference throughput over previous TPU generations.
Scalability: Supports over 100,000 interconnected chips, enabling AI supercomputers of unprecedented scale.
Efficiency: Achieves a 67% energy efficiency boost and up to 2.5x better price-performance for AI training tasks.
Specialization: Optimized for large language models (LLMs) and advanced architectures like Mixture of Experts (MoE).
Applications Across Enterprise and Consumer Markets
Enterprise Use Cases:
Large Enterprises: Training custom LLMs, running simulations, and optimizing marketing campaigns.
SMBs: Accessing domain-specific AI models and pre-packaged solutions for customer engagement and operations.
Consumer Use Cases:
Search: AI-powered enhancements tailored to evolving user needs.
Google Lens: AI-driven shopping tools, navigation, and real-world insights.
AI Agents and AR: Projects like Mariner and Astra push boundaries with browser automation and AI-integrated AR assistants.
Competitive Position and Future Outlook
Google is positioning itself as a dominant force in AI, challenging competitors like NVIDIA:
Trillium TPU vs. NVIDIA GPUs: The Trillium architecture rivals NVIDIA in performance and scalability, enabling groundbreaking AI workloads.
Cloud Strategy: Leveraging its AI infrastructure internally and as a competitive cloud services offering.
Future Prospects:
AI Ecosystem Integration: Google’s push to embed AI throughout its products underpins its "AI-first" vision.
Emerging Markets: Initiatives like AR devices, advanced AI agents, and autonomous vehicles open new frontiers.
Waymo as a Model: Success in self-driving technology highlights Google’s potential to redefine its business beyond search.
Key Insights
Google’s AI strategy is built on robust infrastructure, enterprise services, and consumer integration.
Trillium TPU’s capabilities differentiate Google, offering scalability, efficiency, and performance for AI workloads.
Both enterprise and consumer markets are central to Google's AI expansion, with innovative solutions targeting diverse needs.
The company’s shift beyond search leverages AI to power new industries, products, and markets.
Listen Also
Read Also
With massive ♥️ Gennaro Cuofano, The Business Engineer